FAQs
What are the 3 common types of ERP?
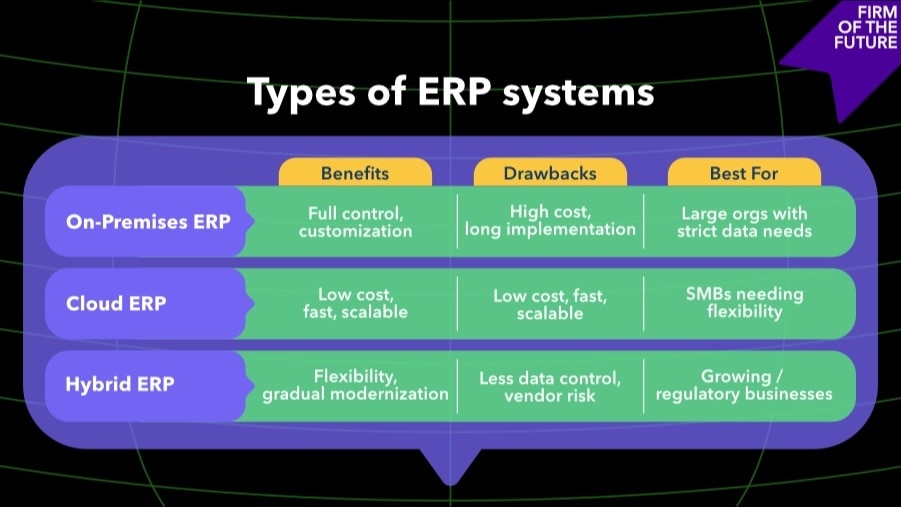
The three primary types of enterprise resource planning systems are on-premise ERP (installed on company servers), cloud ERP (hosted remotely and accessed via internet), and hybrid ERP (combining both approaches).
What is the most common ERP system?
Cloud-based ERPs are the most common system.
What is the difference between ERP and accounting software?
Traditional accounting software focuses solely on financial management—bookkeeping, invoicing, and basic reporting. ERP systems integrate these financial functions with other business operations, such as inventory, HR, CRM, and supply chain management, providing a comprehensive business management solution.
How do ERP systems benefit accountants?
ERPs provide a platform for business intelligence that support client advisory services offerings. They can also help automate routine tasks, provide real-time financial insights, ensure data accuracy across departments, and enable sophisticated reporting and forecasting capabilities.
Is QuickBooks an ERP system?
QuickBooks itself is accounting software, not a full enterprise resource planning solution. However, Intuit Enterprise Suite builds on the QuickBooks platform to deliver ERP functionality, including multi-entity consolidation, customizable reporting dimensions, and industry-specific modules.
Can small businesses use ERP systems effectively?
Absolutely. Modern cloud-based ERP systems are designed with small businesses in mind, offering scalable pricing, faster implementation, and user-friendly interfaces that don't require extensive IT resources.
What industries benefit most from ERP software?
Manufacturing, retail, healthcare, professional services, and construction see significant benefits from ERP implementation due to their complex operations, inventory management needs, and regulatory requirements.
How long does it take to implement an ERP system?
Implementation timelines vary widely—from a few weeks for cloud-based solutions like IES to 6-18 months for complex enterprise systems. Cloud ERPs typically offer the fastest deployments; Intuit Enterprise Suite can generally be implemented within two months.
What are the key modules in an ERP system?
Core ERP modules typically include financial management, inventory control, supply chain management, human resources, CRM, and reporting/analytics. Industry-specific systems add specialized modules for manufacturing, healthcare, retail, or other sectors.
Do ERP systems work for remote teams?
Yes, especially cloud ERP systems, which provide secure access from anywhere with internet connectivity. Modern ERPs support real-time collaboration, mobile access, and role-based permissions—ideal for distributed workforces.
How do cloud ERP systems differ from on-premise ones?
Cloud ERPs offer lower upfront costs, automatic updates, easier scalability, and remote accessibility. On-premise systems provide more control over data and customization but require significant IT infrastructure and maintenance.
What should businesses look for in an ERP vendor?
Look for vendors with proven industry experience, strong implementation support, reliable customer service, and a solid product roadmap. For accountants and advisory firms, prioritize solutions that build on familiar systems (like QuickBooks) so you can confidently guide clients without needing to master a completely new platform.