Data silos and clunky reporting processes slow companies down and can keep important business insights out of reach. Business intelligence (BI) bridges the gaps by transforming how accounting professionals analyze, interpret, and present financial data to their clients.
Business intelligence capabilities within ERP systems can help accountants deliver real-time financial insights, and access automated reporting and predictive analytics that turn raw numbers into strategic roadmaps. Business intelligence capabilities empower you to maximize your impact, interpreting financial signals and translating data into actionable advice that drives your clients forward.
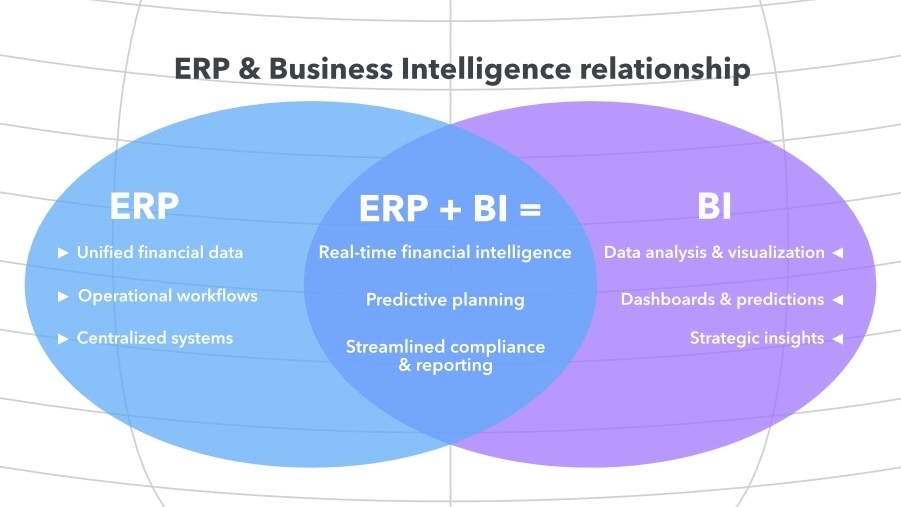
What’s the relationship between an ERP and BI?
Unlocking BI through an ERP integration creates exponential value for accountants and clients. But to appreciate the power of ERP-powered BI, it helps to first understand these systems on their own.
BI is the process of collecting, analyzing, and visualizing data to support smarter decisions. In accounting, it means turning raw financial data into insights that guide day-to-day operations and long-term strategy.
By centralizing data from sources such as sales, operations, and finance, BI helps uncover trends, predict outcomes, and identify areas for improvement. Dashboards and visualizations make complex information easier to act on, while AI-powered analytics can surface patterns that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems serve as the central nervous system of a business, connecting data across departments and workflows. These platforms create a unified view of core financials, including ledgers, accounts payable and receivable, reporting, and compliance, and operational functions such as inventory and procurement.
ERP-integrated business intelligence brings these capabilities together. Instead of exporting ERP data into external BI tools, integrated solutions enable real-time analysis directly within the ERP system. This reduces delays, minimizes manual work, and keeps insight as close to the data source as possible.